




As a company considers expanding to new markets, international business strategies must be put in place for that plan to be effective. This is the first installment of an international business strategies series that will take a deep dive into translational, multi-domestic, global, and international strategies used to target new markets within international borders.
All the strategies mentioned above require a specific level of commitment around four main factors. Those factors are local responsiveness, global integration, standardization, and customization.
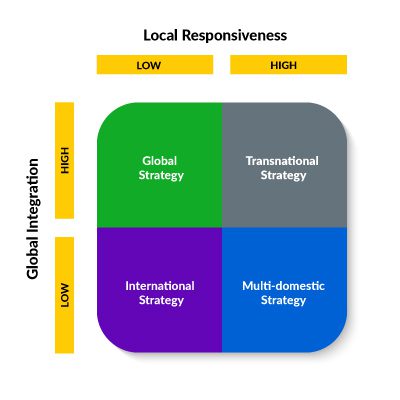
Before determining the best approach for global expansion, it’s important to understand the four primary global business strategy pillars:
Local Responsiveness
Local responsiveness refers to a company that localizes its products and services to meet conditions and nuances in other countries.
Global Integration
Global integration refers to a company’s local presence in the global market and the degree to which it can use the same products and services in other countries.
Standardization
Standardization refers to how a company does a “one size fits all” for the same products and services in other countries.
Personalização
Customization refers to the process through which a standard message, procedure, or offering may be adapted according to the context or market in which it will be used.
A transnational strategy places equal importance on global integration and local responsiveness. This makes it an ideal strategy for companies that want to grow their global presence while ensuring they meet the needs of a multilingual, multicultural audience.
Transnational strategies typically involve large companies with different subsidiaries, branches, or offices across multiple global markets. The challenge is determining what stays the same across all global communications and procedures vs. where adaptations from local subsidiaries in global markets are adjusted or allowed. Finding the right balance between local responsiveness and global integration is going to be unique for every organization.
Companies spearheading a transnational strategy know when to allow global branches to adjust and make customizations and when not to. This means having clear directions on all international activities and operations.
There are several international business strategies to compare, here are a few examples:
A transnational strategy is best for companies operating in diverse international markets where both cost control and localization are critical. For example, global brands like Coca-Cola or McDonald's standardize core products while customizing advertising, packaging, and messaging for local audiences.
This strategy enables your business to:
Compete on a global scale while respecting local norms.
Maintain brand consistency across regions.
Use centralized systems for cost efficiency.
Deliver a localized experience to boost relevance and customer trust.
Build a scalable global content strategy for multilingual audiences.
However, executing a transnational strategy takes more effort than other models. You must decide which elements to centralize and which to localize-from pricing to website translation to product features.
Transnational businesses must operate through an organized network of subsidiaries across multiple countries. Each subsidiary needs to understand its local customers' preferences and combine the resources provided by the head office to adapt products and services to local preferences.
With a proper transnational strategy, multinational corporations can leverage the benefits of standardization without sacrificing local responsiveness in different countries. They operate at a high level of communication, knowledge, and productivity to meet strategic objectives across various markets.
It's crucial to understand that the strategies that may have worked in one market (or company) may not be successful in another. The more agile and receptive you are to buyer tendencies in different regions, the faster you can implement changes.
Digital transformation adds new complexity to global expansion. Brands must provide consistent messaging while personalizing customer experiences across channels like websites, mobile apps, support portals, and social media.
To execute your transnational strategy successfully, you need technology that supports both scale and flexibility. A modern website translation solution can:
Centralize content management across regions.
Empower local teams to customize specific web pages or promotions.
Speed up translation without compromising quality.
Support SEO localization to drive global visibility.
Language and cultural relevance are essential in connecting with global audiences. Companies that invest in high-quality multilingual content and website translation see stronger brand engagement and better ROI across international markets.
Your global content strategy must ensure that translated material aligns with local tone, style, and expectations. This goes beyond just words-it includes visuals, CTAs, legal requirements, and even payment methods.
With the right transnational strategy, you can enter new markets, connect with diverse global audiences, and drive sustainable growth worldwide. There are many approaches to start executing a successful transnational strategy—developing new brands, investing in localized marketing campaigns, and testing new products are some examples. But regardless of your go-to-market strategy, your company should seek to pursue robust translation workflow processes and high translation quality. Efficient communication will play a significant role in your success.
MotionPoint helps global brands launch, manage, and scale multilingual websites and customer experiences. Our adaptive translation technology supports your localization strategy while preserving global brand consistency.
Special Offer: When you launch one language (like Canadian French), we’ll give you a second language (like European French) free for a limited time. Let’s build your global presence—one market at a time.